Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is where there's chronic inflammation of the gut wall with periods of remission and exacerbation. Patients present with:
Diarrhoea
Mucous/blood in stool
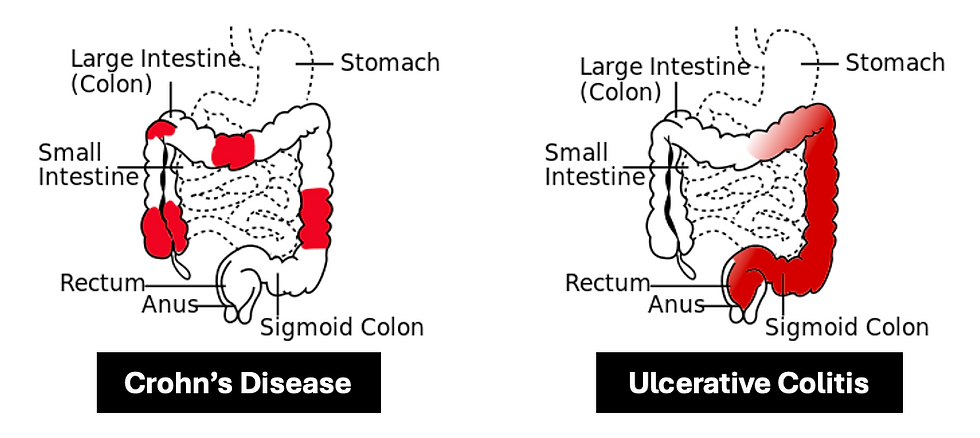
Abdominal pain - LLQ with UC, RLQ with Crohn’s
Weight loss
Differentials - IBS (diagnosis of exclusion), Diverticulitis, and Appendicitis.
Investigations:
Bloods - FBC, U&E, LFT, CRP, ESR, INR, Ferritin, B12, Folate, TFT, Albumin
Stool culture - exclude c.diff
Faecal Calprotectin - Raised in IBD, therefore differentiating it from IBS
N.B. Faecal calprotectin can also be raised with NSAIDs and PPIs.
Crohn’s:
This is characterised by transmural inflammation, which affects the entire GI tract. The terminal ileum and proximal colon (RLQ) is the most common area affected. The manifestations of this disease are:
Mouth ulcers
Perianal abscesses/fistulas, Skin tags
Erythema nodosum
Anterior uveitis
Gallstones
Smoking is a major risk factor here.
Investigations:
Colonoscopy - Skip lesions, Cobblestone appearance (due to ulceration and mural oedema), Non-caseating granulomas
CT/MRI - Bowel wall thickening, Increased bowel wall brightness (damaged area takes up more contrast), Comb sign (Hyper-vascularity of mesentery)
Complications:
Strictures
Fistulas
Adhesions
Management:
Conservative - Smoking cessation
Induce remission - Steroids (1st line) e.g. pred, hydro
Azathioprine or Methotrexate 2nd line
Maintain remission - Azathioprine (1st line)
Methotrexate 2nd line
Ulcerative Colitis:
This is characterised by inner mucosal inflammation, which only affects the colon. The manifestations of this disease are:
PR blood and mucous
Anterior uveitis
Investigations:
Colonoscopy - Continuous inflammation, Crypt abscesses (full of neutrophils)
CT/MRI
Thumbprinting - thickened mucosal folds due to bowel wall oedema)
Lead piping - occurs in chronic cases as bowel becomes featureless w/loss of haustral marking, luminal narrowing and bowel shortening

Complications:
Toxic megacolon
Colorectal cancer
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Cholangiocarcinoma
Stricture
Management:
Induce remission:
Mild-moderate disease - Topical/Oral Aminosalicylate (1st line) e.g. Mesalazine. Consider adding prednisolone if no response in 72 hours.
Severe disease - IV Prednisolone (1st line). Add IV Ciclosporin or consider surgery if no response in 72 hours.
Maintain remission - Topical/Oral Aminosalicylate
Curative - Total panproctocolectomy